Uncover South Korea’s recent political turmoil: the martial law declaration, its swift repeal, public reactions, and the implications for democracy in Asia.
Background
Political tensions have been simmering in South Korea for months. Opposition leaders accused the government of authoritarian behavior, culminating in martial law. This decision evoked haunting memories of past military crackdowns, notably the 1980 Gwangju Uprising, a dark chapter in South Korea’s history..
Reference :- Gwangju Uprising
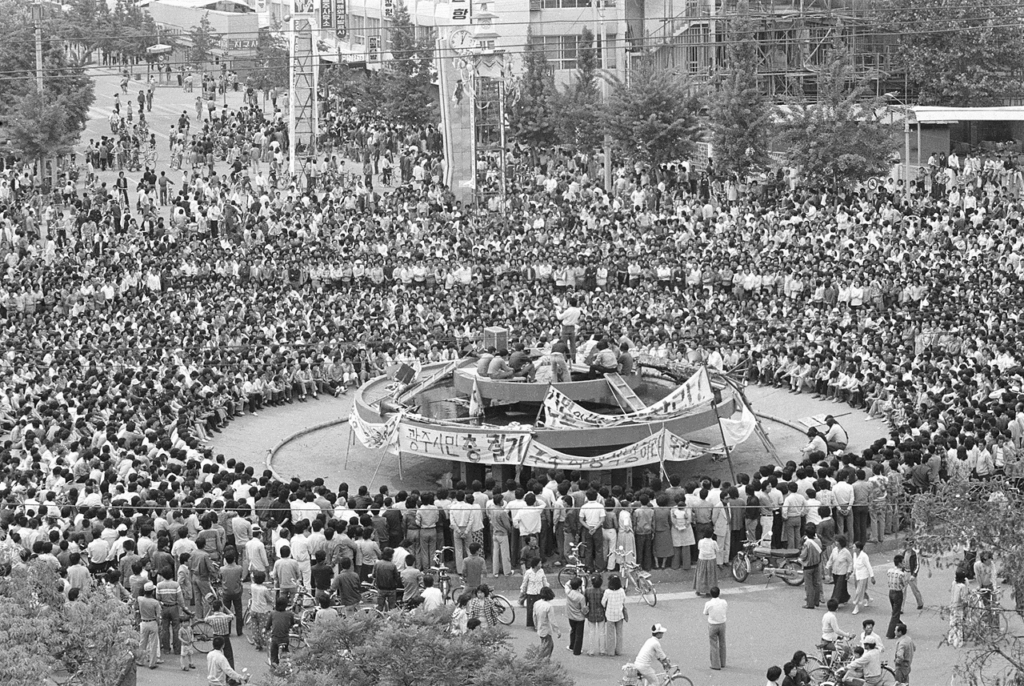
This undated handout photo taken in May 1980 and provided by the 5.18 Memorial Foundation shows protesters gathering in a central square during the pro-democracy uprising in the southern city of Gwangju. — AFP photo
What Happened?
On December 3, 2024, South Korean President Yoon Suk Yeol declared martial law, citing the need to eliminate what he described as “anti-state” forces amid growing opposition protests. The move was seen by many as a drastic measure to assert control over political opposition and curb dissent. In his address, President Yoon accused opposition parties of sympathizing with North Korea and vowed to take strong action against perceived internal threats. This declaration, which temporarily placed the country under military rule, sent shockwaves through South Korean society.
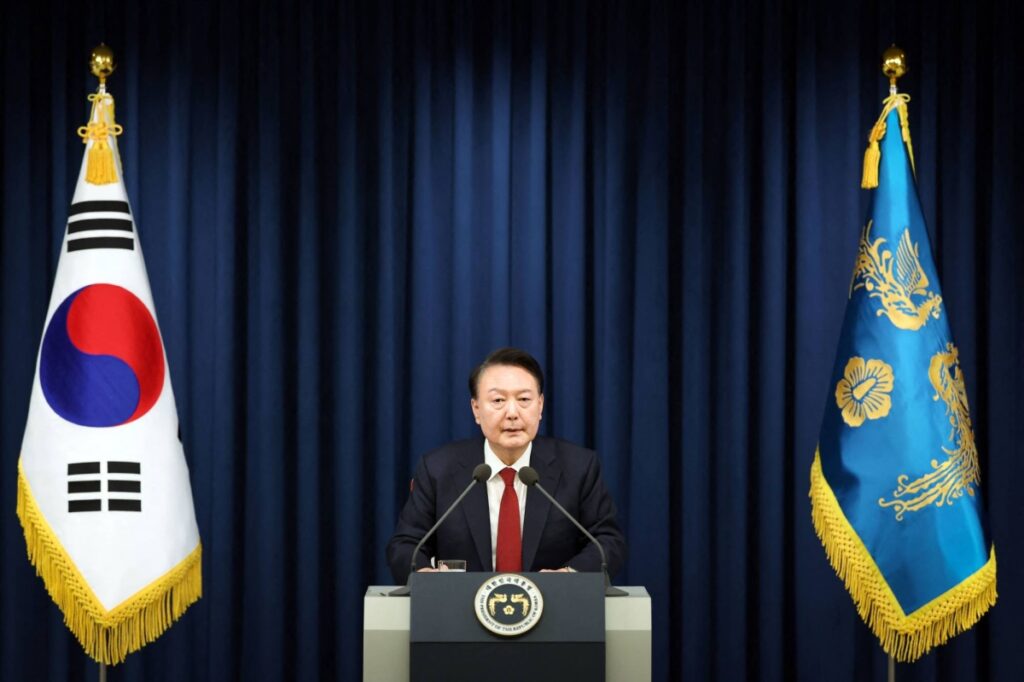

South Korean President Yoon Suk Yeol delivering a speech to declare martial law in Seoul
December 3 , 2024
However, the declaration of martial law was quickly reversed. Within hours, the National Assembly—where President Yoon’s party does not hold a supermajority—moved swiftly to reject the measure. The vote was decisive, with lawmakers overwhelmingly opposing it by a 190 to 0 margin, leading to the immediate revocation of martial law. This rapid parliamentary response was viewed as a powerful statement in defense of South Korea’s democratic principles and a firm rejection of any return to authoritarian rule.
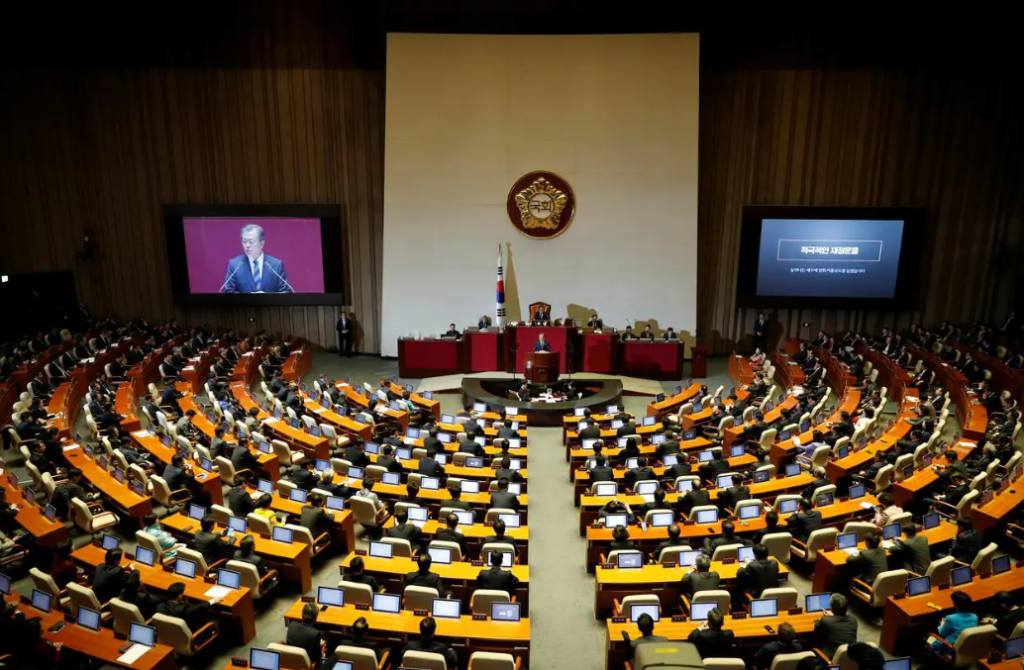

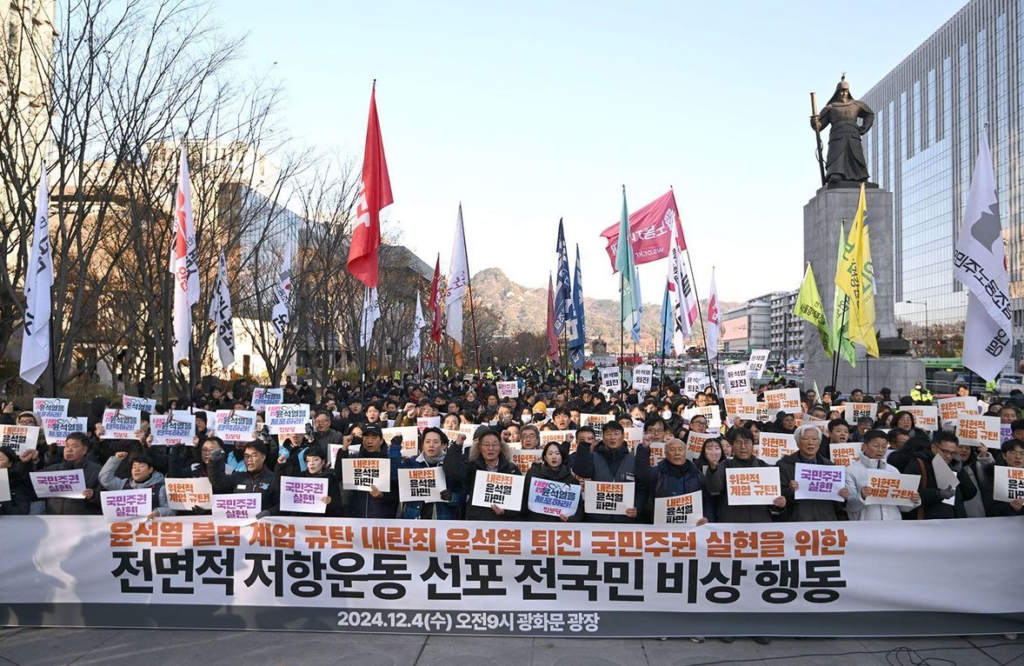
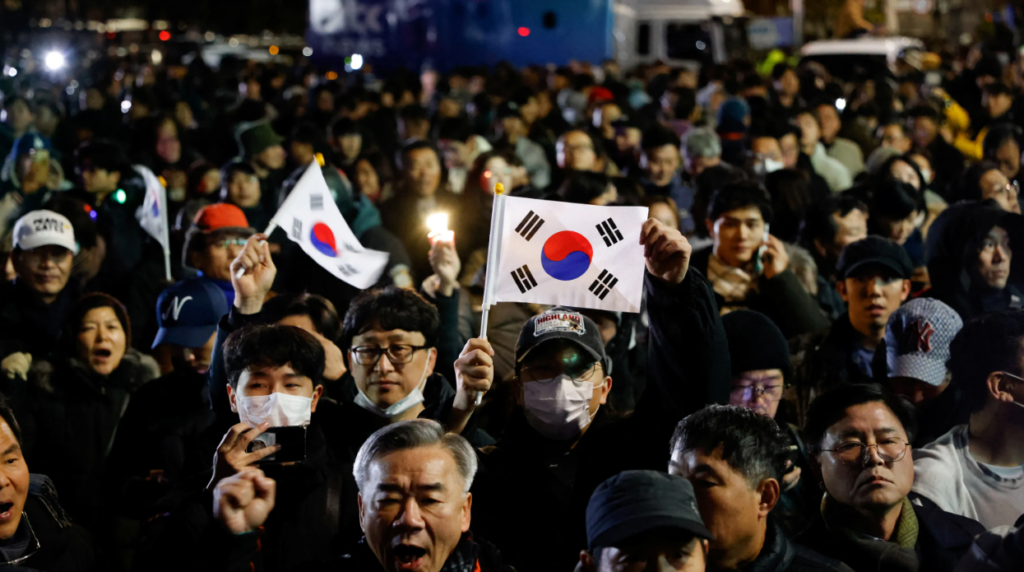
The martial law lasted only about six hours, yet its impact was profound and long-lasting. Almost immediately, protests erupted across South Korea. Citizens filled the streets, holding candlelight vigils to voice their concerns over the potential erosion of democratic freedoms. This rapid and widespread public response underscored the deep political divisions within the country and highlighted the strong commitment to protecting South Korea’s democratic institutions.
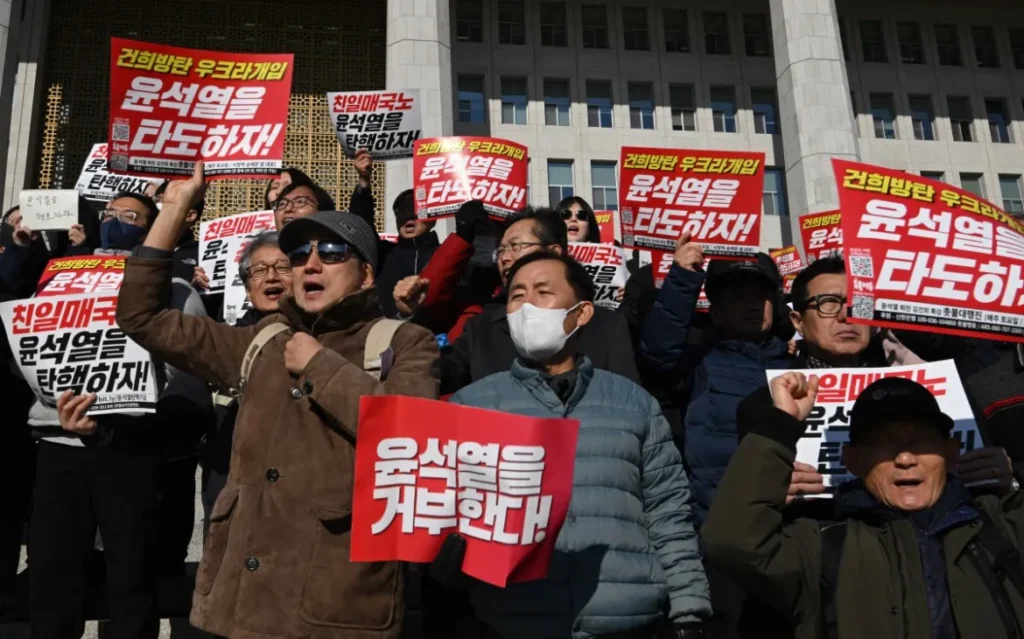
Public Reactions
The streets were filled with chants for freedom. Online, hashtags like #SaveSouthKorea trended globally. Citizens demanded accountability, with many recalling South Korea’s painful journey to democracy.


Conclusion
South Korea’s political, economic, and social landscape is constantly evolving, drawing attention from around the world. The country faces a mix of challenges, from rising tensions with North Korea and complex international relations, to shifting economic dynamics and societal changes. Understanding these factors is key to grasping the broader implications for the region and the world.
As South Korea moves forward, balancing domestic struggles with global pressures will be crucial. The country’s role in international security, trade, and diplomacy will be critical in shaping its future path. Adapting to these challenges will determine how South Korea navigates its future trajectory.
For readers, staying informed on these issues is vital not only to understand South Korea’s situation but also to see how interconnected global politics can affect daily life. South Korea’s circumstances reflect larger trends in global geopolitics that are worth keeping an eye on.
“What are your thoughts on this issue? Share in the comments!”
Explore more on this topic :-
2024 South Korean martial law – Wikipedia
What is martial law and what has happened in South Korea? | CNN
Why did South Korea declare martial law and what’s next for President Yoon? | Reuters
Democracy under pressure: unpacking fears of martial law in South Korea – The Korea Times
<- Previous

